Abstract
Background:
The combination of HMA and venetoclax is now standard of care for patients with AML who are not candidates for intensive chemotherapy. Elderly patients are more likely to have secondary AML (sAML), although the presence of an antecedent hematologic malignancy is often not apparent by history. Lindsley et al (Blood, 2015) showed that a somatic mutation in SRSF2, SF3B1, U2AF1, ZRSR2, ASXL1, EZH2, BCOR, or STAG2 is >95% specific for sAML and associated with worse outcomes. While outcomes with HMA/ven in patients meeting standard criteria for sAML have recently been reported (Pullarkat, ASCO 2021), we set out to conduct a real-world analysis of sAML patients receiving HMA/ven, including those with a secondary mutation profile (SMP) as described by Lindsley et al. We hypothesized that-when treated with HMA/ven-outcomes of patients with SMP may be most similar to those with de novo AML.
Methods:
Patients diagnosed with AML at Stanford Cancer Institute from 4/2017-3/2021 and treated with front-line HMA/ven were retrospectively reviewed. These included patients previously treated with HMA monotherapy for an antecedent hematologic malignancy and those who had previously received ≤ 3 cycles of HMA monotherapy for AML. Responses were classified per the modified International Working Group response criteria. Overall survival (OS) was assessed for all patients, and for patients who had a complete response (CR) or CR with incomplete hematologic recovery (CRi), duration of response (DoR) was also assessed. Statistical analyses were performed in R using the logrank test, with hazard ratios (HR) computed using the Cox proportional hazards model. For multivariate analyses, p-values for a specific variable were calculated using Cox proportional hazards regression.
Results:
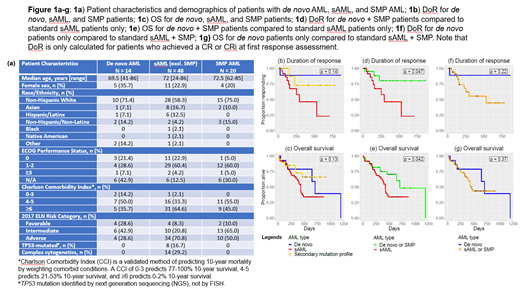
82 patients met criteria for inclusion; 78 had valid response assessments and 49 (62.8%) had achieved a CR or CRi at first response assessment. Median age was 72 years, with 3 patients younger than 60. 62 patients were male, median ECOG performance status (PS) was 1, median Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) was 6, median time to death or end of follow-up from the start of treatment was 366 days, and 58% of patients had adverse risk AML per ELN guidelines. Fig 1a demonstrates demographics for de novo, sAML (excluding SMP), and patients with SMP AML. 13 patients met criteria for AML-MRC, 23 patients had prior history of antecedent hematologic malignancy (18 with MDS or CMML, 5 with MDS/MPN overlap or MPN), 12 had tAML, and 20 patients possessed a SMP and did not meet criteria for the other three categories of sAML. 14 patients with de novo AML were characterized by the absence of any of the above factors. Patients with de novo AML were less likely to have adverse risk disease (29% vs. 64% in others) and had lower CCI scores (mean 5.1 vs. 6.2) but had no significant differences in age, gender, follow-up time, or PS.
There was no statistically significant difference in rates of CR/CRi between the different subgroups or the different types of sAML; 69% of patients with de novo AML, 79% of SMP patients, and 57% of patients with other types of sAML achieved a CR or CRi. However, SMP patients had response durations and OS patterns similar to patients with de novo AML (Fig 1b and 1c), and when grouped with de novo patients, both DoR (HR = 3.5, p = 0.047, Fig 1d) and OS (HR = 2.1, p = 0.042, Fig 1e) were significantly longer than those of the sAML patients. Neither DoR nor OS were significantly longer when the SMP patients were grouped with sAML patients (respectively: HR = 3.3, p = 0.22, Fig 1f; HR = 1.5, p = 0.37, Fig 1g). In multivariate Cox proportional regression adjusting for age, ELN risk category, CCI, and PS, worse OS for sAML patients was maintained relative to the SMP and de novo patients (HR 2.9, p = 0.036), although the difference in DoR was no longer significant (HR 4.4, p= 0.10).
Conclusions:
Patients meeting standard definitions of sAML had worse outcomes than those with de novo AML when treated with HMA/ven in a retrospective, real-world analysis. Although a secondary mutation profile as described by Lindsley et al may be helpful in identifying patients with sAML, when treated with HMA/ven, patients with this profile have outcomes that align more closely with those of patients with de novo AML.
Mannis: Astex, Forty Seven Inc/Gilead, Glycomimetics, and Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; AbbVie, Agios, Astellas Pharma, Bristol Myers Squibb, Genentech, MacroGenics, Pfizer, and Stemline: Consultancy.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal